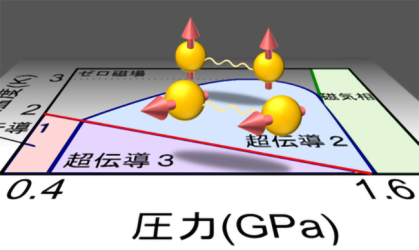
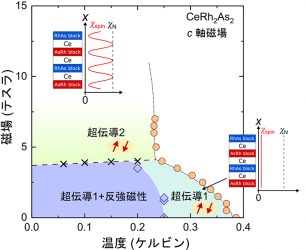
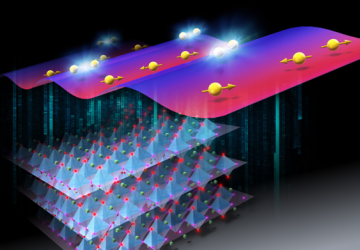
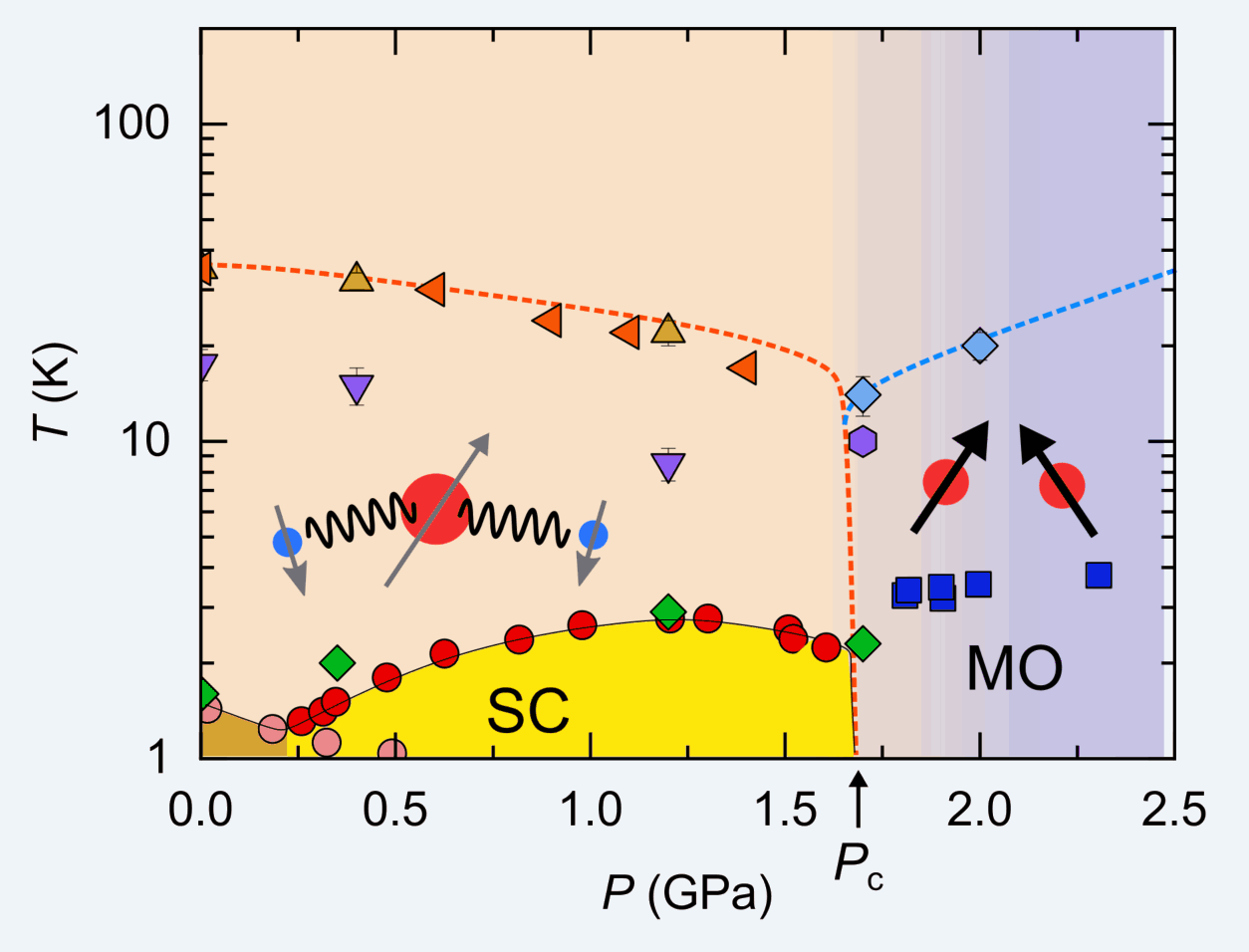
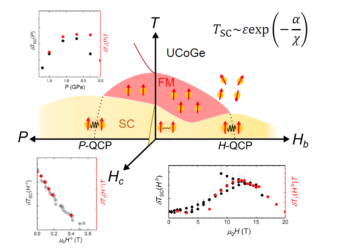
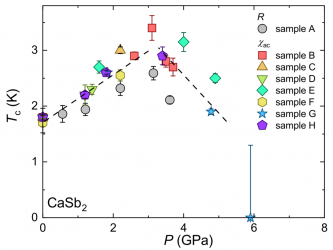
Superconducting (SC) state has spin and orbital degrees of freedom, and spin-triplet superconductivity shows multiple SC phases because of the presence of these degrees of freedom. However, the observation of spin-direction rotation occurring inside the SC state (SC spin rotation) has hardly been reported. Uranium ditelluride, a recently found topological superconductor, exhibits various SC phases […]
![]()