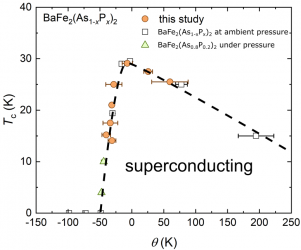
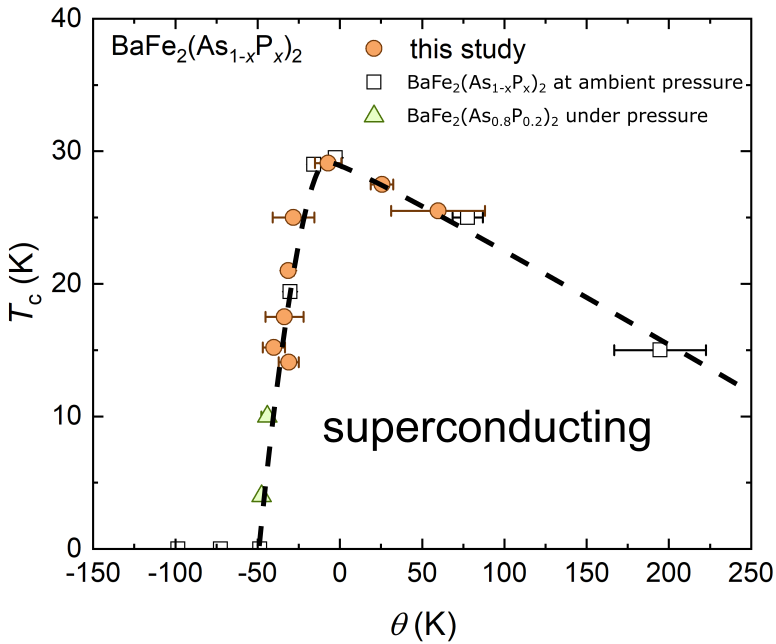
The iron-based superconductor BaFe 2 As 2 suppresses antiferromagnetism by various dopings and pressures and develops superconductivity. We applied pressure to BaFe 2 (As 1- x P x ) 2 with part of As replaced by equivalent P and searched for the essential parameters that govern the superconducting transition temperature by changing two parameters, the P substitution amount and the pressure. As shown in the figure, the superconducting transition temperature at various parameters can be scaled by the distance θ from the antiferromagnetic quantum critical point. This indicates that the superconducting transition temperature is closely related to θ, that is, antiferromagnetic fluctuations and superconductivity are strongly correlated.
This research is collaborative research with Kyoto University Quantum Condensed Matter Group, University of Tokyo. The results are published in the Phys. Rev. B magazine as Rapid Communication . Click here for the preprint .
Article information
Shunsaku Kitagawa, Takeshi Kawamura, Kenji Ishida, Yuta Mizukami, Shigeru Kasahara, Takasada Shibauchi, Takahito Terashima, and Yuji Matsuda Universal relationship between low-energy antiferromagnetic fluctuations and superconductivity in BaFe 2 (As 1- x P x ) 2 Phys. Rev. B 100, 060503 (Aug. 2019).
![]()